In today’s digital age, data centers play a crucial role in storing and managing vast amounts of information for businesses. As such, it is imperative for data center operators to ensure that their facilities are equipped with reliable backup power sources to prevent costly downtime and data loss in the event of a power outage. One of the most effective solutions for ensuring continuous operation of a data center is investing in a backup generator.
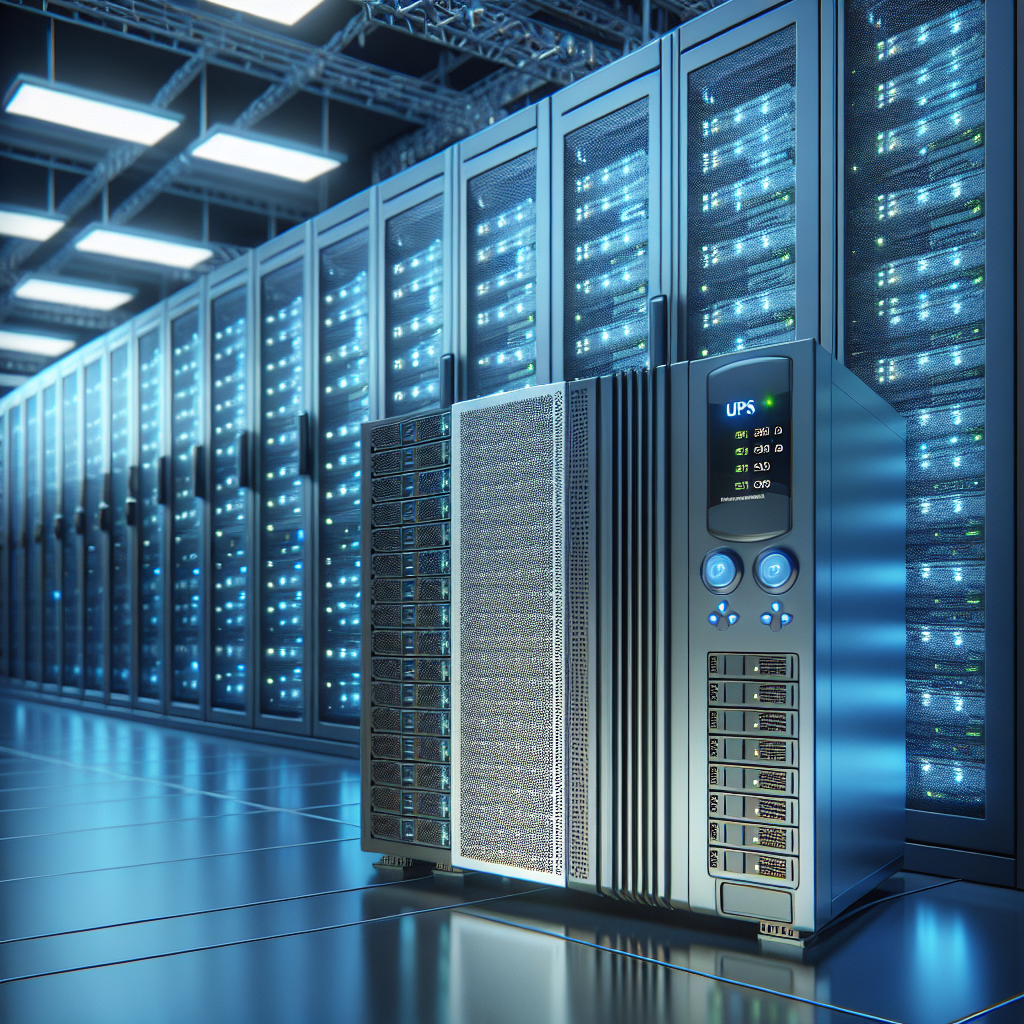
A backup generator is a reliable source of secondary power that can automatically kick in when the main power source fails. This ensures that critical systems and equipment in the data center remain operational, minimizing the risk of data loss and downtime. Here are some of the key benefits of investing in a backup generator for your data center:
1. Continuous Operation: One of the primary benefits of having a backup generator for your data center is the ability to maintain continuous operation even during power outages. This is essential for businesses that rely on their data centers to provide uninterrupted services to their customers.
2. Data Protection: Data centers store sensitive and critical information for businesses, making data loss a major concern in the event of a power outage. A backup generator ensures that data is protected and that there is no risk of losing valuable information during an outage.
3. Cost Savings: Downtime can be extremely costly for businesses, with studies showing that the average cost of data center downtime is around $9,000 per minute. By investing in a backup generator, businesses can avoid these hefty costs associated with downtime and ensure that their operations remain uninterrupted.
4. Enhanced Reliability: Backup generators are designed to provide a reliable source of power during emergencies, ensuring that critical systems and equipment in the data center remain operational. This enhances the overall reliability of the data center and minimizes the risk of disruptions.
5. Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data protection and uptime requirements. Investing in a backup generator can help businesses comply with these regulations and avoid potential fines or penalties for non-compliance.
In conclusion, investing in a backup generator for your data center is a wise decision that can help protect your valuable data, ensure continuous operation, and save your business from costly downtime. With the numerous benefits that a backup generator provides, it is a crucial investment for any business that relies on its data center for its operations.