Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Data storage
The Benefits of Upgrading to a Solid-State Drive
Upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD) is one of the best investments you can make for your computer. SSDs offer a wide range of benefits that can greatly improve the performance and efficiency of your system. From faster boot times to better overall speed and responsiveness, here are some of the key benefits of upgrading to an SSD.Improved Performance: One of the biggest advantages of upgrading to an SSD is the significant improvement in performance. SSDs are much faster than traditional hard drives, which means that your computer will boot up faster, applications will load quicker, and overall system performance will be greatly enhanced. This can make a big difference in your day-to-day computing experience, allowing you to work more efficiently and effectively.
Faster Boot Times: SSDs can drastically reduce the time it takes for your computer to boot up. With an SSD, you can expect your system to start up in a matter of seconds, compared to the minutes it can take with a traditional hard drive. This can save you valuable time and make your computer more convenient to use.
Improved Reliability: SSDs are more reliable than traditional hard drives because they have no moving parts. This means that they are less susceptible to physical damage and are less likely to fail over time. With an SSD, you can have peace of mind knowing that your data is safe and secure.
Energy Efficiency: SSDs are more energy efficient than traditional hard drives, which can help to prolong the battery life of laptops and other portable devices. This can be especially beneficial for users who are constantly on the go and need their devices to last as long as possible.
Quieter Operation: Because SSDs have no moving parts, they operate more quietly than traditional hard drives. This can help to reduce noise levels and create a more peaceful computing environment.
Overall, upgrading to an SSD can provide a wide range of benefits that can greatly improve the performance and efficiency of your computer. Whether you are looking to boost speed, enhance reliability, or simply make your system more energy efficient, an SSD is a smart investment that can pay off in the long run. So if you are looking to take your computing experience to the next level, consider upgrading to a solid-state drive today.
The Evolution of Data Storage: From Floppy Disks to Cloud Computing
Data storage has come a long way since the days of floppy disks and CDs. The evolution of data storage has been a fascinating journey, with technology advancing at a rapid pace to meet the growing demands of businesses and individuals alike. From the early days of physical storage devices to the era of cloud computing, the way we store and access data has been revolutionized in recent years.In the early days of computing, floppy disks were the go-to storage solution for saving documents and files. These small, portable disks could hold a limited amount of data, typically around 1.44 MB. As technology advanced, CDs and DVDs became popular for storing larger files, such as music and videos. However, these physical storage devices had their limitations, including susceptibility to damage and loss of data.
The next major advancement in data storage came with the introduction of external hard drives and USB flash drives. These devices offered larger storage capacities and faster data transfer speeds, making them ideal for backing up important files and transferring data between devices. However, they still required physical connection to a computer, limiting their portability and accessibility.
The rise of cloud computing has been a game-changer in the world of data storage. Cloud storage services such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and iCloud allow users to store and access their data remotely over the internet. This means that users can access their files from any device with an internet connection, making data storage more convenient and flexible than ever before.
Cloud storage offers several advantages over traditional physical storage devices, including scalability, accessibility, and security. With cloud storage, users can easily expand their storage capacity as their needs grow, without the need to invest in additional hardware. Additionally, cloud storage providers offer robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
The evolution of data storage from floppy disks to cloud computing has transformed the way we store and access information. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that new innovations in data storage will continue to emerge, offering even greater capabilities and efficiency. In the meantime, cloud computing remains a reliable and convenient solution for managing and storing data in today’s digital age.

The Evolution of Magnetic Storage: From Floppy Disks to Solid-State Drives
Magnetic storage has come a long way since the days of floppy disks. These iconic storage devices were once the go-to option for storing and transferring data, but with advancements in technology, they have been largely replaced by more efficient and high-capacity options such as solid-state drives (SSDs).Floppy disks were first introduced in the 1970s and quickly became popular due to their portability and ease of use. However, their limited storage capacity and slow read/write speeds meant that they were quickly surpassed by newer storage technologies.
The next major innovation in magnetic storage came in the form of hard disk drives (HDDs). These devices used magnetic disks to store data and were much faster and more reliable than floppy disks. HDDs quickly became the standard for storing large amounts of data, and are still widely used today in desktop computers, laptops, and servers.
In recent years, solid-state drives have emerged as the new standard for storage technology. Unlike HDDs, which use spinning disks, SSDs use flash memory to store data. This allows them to be much faster, quieter, and more durable than traditional HDDs. SSDs also have the added benefit of being more energy efficient, which can lead to longer battery life in laptops and other portable devices.
While SSDs are more expensive than HDDs, the price of flash memory has been steadily decreasing, making them more accessible to consumers. As a result, many new computers and laptops now come equipped with SSDs as standard, and they are also commonly used in high-performance gaming systems and servers.
The evolution of magnetic storage from floppy disks to solid-state drives has been a remarkable journey. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see even more improvements in storage technology in the future. Who knows what the next generation of storage devices will look like? Only time will tell.

The Evolution of Storage Devices: From Floppy Disks to Cloud Storage
The Evolution of Storage Devices: From Floppy Disks to Cloud StorageIn the early days of computing, storage devices were bulky and limited in capacity. One of the first storage devices to gain popularity was the floppy disk, which was introduced in the 1970s. Floppy disks were small, portable, and could store a few megabytes of data. However, they were easily damaged and had a limited lifespan.
As technology advanced, storage devices became smaller and more efficient. In the 1980s, the hard disk drive (HDD) was introduced, offering much larger storage capacity than floppy disks. HDDs were internal components of computers and were used to store large amounts of data, such as operating systems, applications, and files.
In the 1990s, the compact disc (CD) and digital versatile disc (DVD) became popular storage devices for storing music, movies, and software. These optical discs had larger storage capacities than floppy disks and were more durable. However, they were still physical media that required physical storage space.
The early 2000s saw the rise of flash memory devices, such as USB drives and SD cards. These devices were smaller, faster, and more durable than previous storage devices. They could store large amounts of data and were easily portable. Flash memory devices quickly became the preferred storage solution for many users.
In recent years, cloud storage has revolutionized the way we store and access data. Cloud storage allows users to store their data remotely on servers maintained by third-party providers. This eliminates the need for physical storage devices and allows users to access their data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud storage offers several advantages over traditional storage devices, including scalability, accessibility, and security. Users can easily expand their storage capacity as needed, access their data from any device, and rest assured that their data is safe and secure.
The evolution of storage devices has come a long way from floppy disks to cloud storage. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative storage solutions to emerge in the future. Whether it’s storing data on a physical device or in the cloud, one thing is certain: storage devices will continue to play a crucial role in our digital lives.

The Evolution of Disk Drives: From Floppy Disks to Solid-State Drives
Disk drives have come a long way since the early days of computing. From the bulky floppy disks of the 1970s to the sleek solid-state drives of today, the evolution of storage technology has been nothing short of remarkable.The first commercially available disk drives were introduced in the late 1950s and early 1960s. These early disk drives used magnetic storage to store data on spinning disks, and were incredibly large and expensive. The introduction of the floppy disk in the 1970s revolutionized the way data was stored and accessed. Floppy disks were smaller, more portable, and could store more data than their predecessors, making them a popular choice for personal computers.
However, floppy disks had their limitations. They were slow, prone to data corruption, and had limited storage capacity. As technology advanced, new forms of storage media were introduced, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and optical disks. HDDs used spinning platters to store data and offered much greater storage capacity than floppy disks. Optical disks, such as CDs and DVDs, used lasers to read and write data, providing even more storage options for consumers.
The next major advancement in disk drive technology came with the introduction of solid-state drives (SSDs). SSDs use flash memory to store data, eliminating the need for moving parts and significantly increasing read and write speeds. SSDs are also more durable and reliable than traditional HDDs, making them a popular choice for high-performance computing applications.
Today, SSDs are widely used in laptops, desktops, and servers, offering faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and improved overall performance. In addition, SSDs are becoming more affordable, making them accessible to a wider range of consumers.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of disk drives is uncertain. Some experts predict that SSDs will eventually replace HDDs as the dominant form of storage media, while others believe that new technologies, such as holographic storage or DNA storage, will revolutionize the way data is stored and accessed.
Regardless of what the future holds, one thing is certain: the evolution of disk drives has been a fascinating journey, from the clunky floppy disks of the past to the lightning-fast SSDs of today. And who knows what the next chapter in the story of storage technology will bring?
Understanding the Basics of Hard Drives: A Comprehensive Guide
Whether you’re a computer enthusiast or just an average user, understanding the basics of hard drives is essential in today’s digital age. Hard drives are the primary storage device in most computers, where all your files, programs, and operating system are stored. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about hard drives, from their types and components to how they work and how to choose the best one for your needs.Types of Hard Drives
There are two main types of hard drives: HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) and SSDs (Solid State Drives). HDDs are the traditional type of hard drive that uses spinning magnetic disks to store data. They are typically cheaper and have larger storage capacities compared to SSDs. However, they are slower and more prone to mechanical failure.
SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory to store data, making them faster, more durable, and energy-efficient. They are becoming increasingly popular in modern computers due to their superior performance. While they are more expensive and have smaller storage capacities compared to HDDs, the benefits they offer make them a worthwhile investment for many users.
Components of a Hard Drive
Regardless of the type, all hard drives consist of several key components. The most important ones include:
– Platters: These are the circular disks inside the hard drive where data is stored. Each platter has a magnetic coating that stores data in the form of 1s and 0s.
– Read/Write Heads: These are tiny components that move over the platters to read and write data. They are responsible for retrieving and storing information on the hard drive.
– Actuator Arm: This is the mechanism that moves the read/write heads across the platters. It allows the heads to access different areas of the disk to retrieve or store data.
– Controller Board: This is the circuit board that manages the operation of the hard drive. It controls the movement of the actuator arm, reads and writes data, and communicates with the computer’s operating system.
How Hard Drives Work
When you save a file on your computer, the data is stored on the hard drive in binary code (1s and 0s) using magnetic fields. The read/write heads move over the platters to access the data, and the controller board manages the process of reading and writing data. When you access a file, the read/write heads locate the data on the platters and retrieve it, allowing you to view or edit the file.
Choosing the Right Hard Drive
When it comes to choosing a hard drive, there are several factors to consider, including storage capacity, speed, reliability, and price. If you need a large amount of storage for a lower cost, an HDD may be the best option for you. However, if you prioritize speed and durability, an SSD may be a better choice.
Ultimately, the best hard drive for you will depend on your specific needs and budget. It’s important to do your research and consider the pros and cons of each type of hard drive before making a decision.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of hard drives is crucial for anyone who uses a computer. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your current hard drive or purchase a new one, knowing the types, components, and how they work will help you make an informed decision. By considering your storage needs, performance requirements, and budget, you can choose the right hard drive that meets your needs and enhances your computing experience.
The Evolution of HDD Technology: A Brief History
The Evolution of HDD Technology: A Brief HistoryHard disk drives (HDDs) have been an essential component of computers for decades, providing a crucial storage solution for digital data. Over the years, HDD technology has evolved significantly, with improvements in capacity, speed, and reliability. In this article, we will explore the history of HDD technology and the key milestones that have shaped its development.
The first commercially available HDD was the IBM 350, introduced in 1956. It had a storage capacity of just 3.75 megabytes and was the size of two refrigerators. Despite its limited capacity and size, the IBM 350 represented a significant advancement in data storage technology.
In the 1970s and 1980s, HDD technology continued to improve, with manufacturers such as Seagate and Western Digital introducing smaller, more efficient drives with higher storage capacities. By the late 1980s, HDDs were becoming more commonplace in personal computers, providing users with a convenient and reliable storage solution.
The 1990s saw further advancements in HDD technology, with the introduction of faster spinning speeds and higher data transfer rates. The development of the IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) interface also made it easier for users to install and use HDDs in their computers.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of Serial ATA (SATA) and Solid State Drives (SSDs) began to challenge the dominance of traditional HDDs. SSDs offered faster read and write speeds and were more durable than HDDs, making them popular choices for high-performance computing applications.
Despite the competition from SSDs, HDD technology has continued to evolve, with manufacturers pushing the limits of storage capacity and data transfer speeds. Today, HDDs are available in capacities of up to 18 terabytes, making them ideal for storing large amounts of data such as photos, videos, and music.
Looking ahead, the future of HDD technology is likely to focus on improving energy efficiency, reliability, and durability. As data storage needs continue to grow, HDD manufacturers will need to innovate to meet the demands of consumers and businesses.
In conclusion, the evolution of HDD technology has been a remarkable journey, from the bulky and limited storage capacities of the early days to the high-capacity, high-speed drives of today. As technology continues to advance, HDDs will remain a crucial component of data storage solutions, providing a reliable and cost-effective option for storing and accessing digital data.
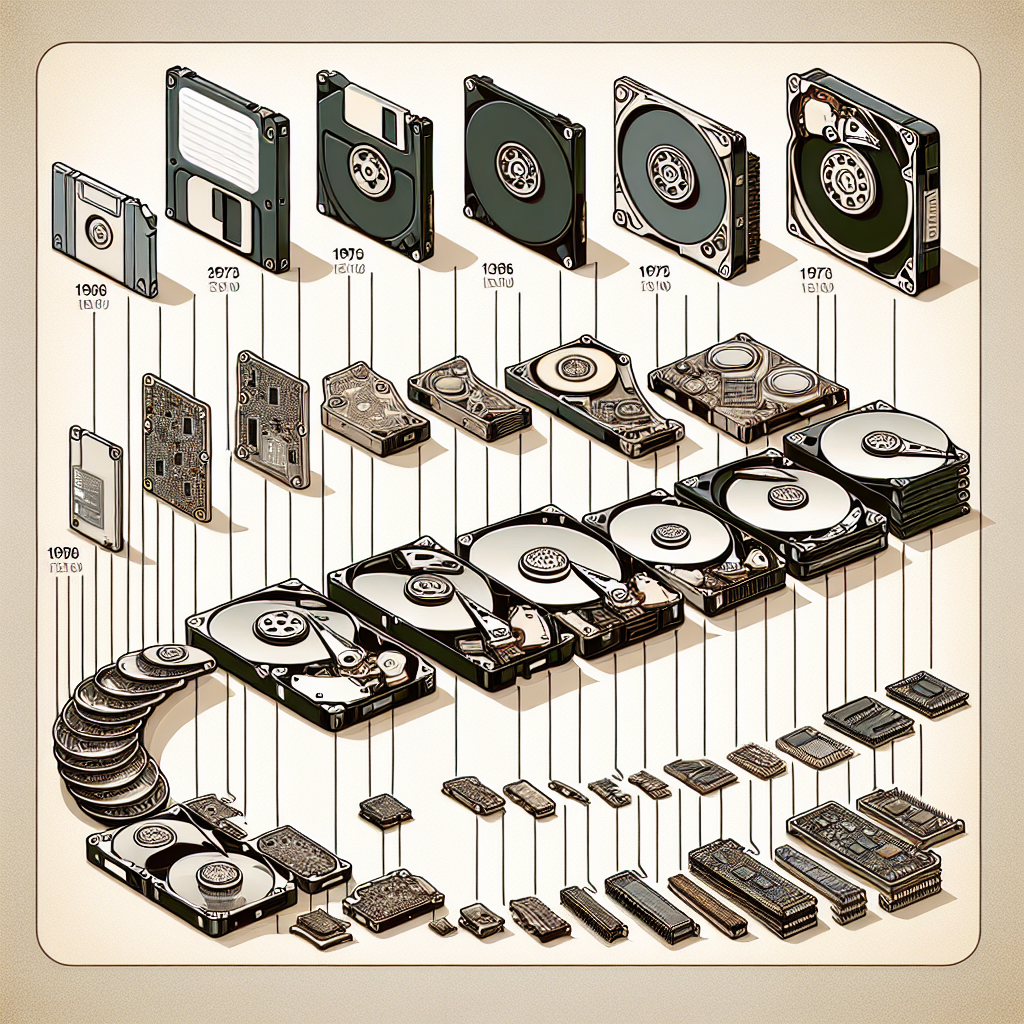
The Evolution of Hard Disk Drives: From Floppy Disks to Solid State Drives
The Evolution of Hard Disk Drives: From Floppy Disks to Solid State DrivesThe evolution of hard disk drives (HDDs) has been a fascinating journey that has revolutionized the way we store and access data. From the early days of floppy disks to the modern solid state drives (SSDs), HDDs have come a long way in terms of storage capacity, speed, and reliability.
The first commercially available HDD was the IBM 350 Disk Storage Unit, which was introduced in 1956. This massive device had a storage capacity of just 3.75 MB and was about the size of two refrigerators. It used a series of spinning disks coated with magnetic material to store data, a technology that would become the foundation for all future HDDs.
In the 1980s, floppy disks became popular as a portable storage solution for personal computers. These flexible plastic disks had a storage capacity of just 1.44 MB and were prone to data corruption and physical damage. Despite their limitations, floppy disks were widely used until the late 1990s when they were replaced by more reliable and higher-capacity HDDs.
The introduction of the first solid state drives (SSDs) in the early 2000s marked a major milestone in the evolution of HDDs. Unlike traditional HDDs, SSDs use flash memory chips to store data, making them faster, more reliable, and more energy-efficient. SSDs also have a smaller form factor and are less prone to physical damage, making them ideal for portable devices like laptops and smartphones.
Today, SSDs have largely replaced traditional HDDs in many applications, thanks to their superior performance and reliability. SSDs can achieve read and write speeds that are up to ten times faster than HDDs, making them ideal for gaming, video editing, and other demanding tasks. SSDs also have a longer lifespan and consume less power, making them a greener alternative to traditional HDDs.
Despite the rise of SSDs, traditional HDDs still have a place in the market, especially for applications that require large storage capacities at a lower cost. HDDs continue to be used in data centers, servers, and other high-capacity storage solutions where cost per gigabyte is a critical factor.
The evolution of hard disk drives from floppy disks to solid state drives has been a testament to the ingenuity and innovation of the technology industry. As we continue to demand faster, more reliable, and more efficient storage solutions, it is exciting to think about what the future holds for HDDs and the next generation of storage technologies.
