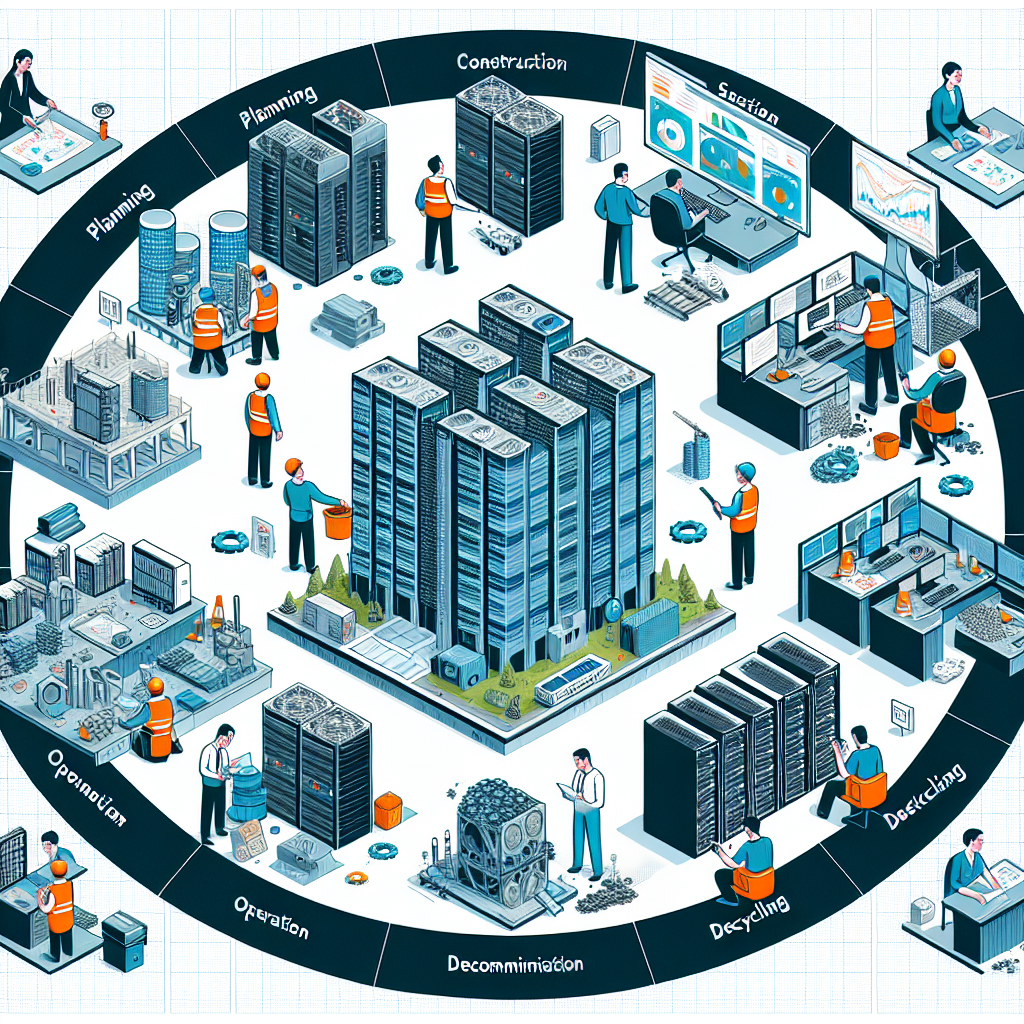
Data centers play a crucial role in the functioning of businesses and organizations in the digital age. These facilities are responsible for storing, processing, and managing large amounts of data that are essential for daily operations. However, managing a data center involves more than just setting up servers and keeping them running smoothly. It also involves planning and executing a comprehensive lifecycle management strategy that encompasses various stages from planning to decommissioning.
The data center lifecycle management process begins with the planning stage. During this phase, organizations need to determine their data center requirements based on their current and future needs. This includes assessing the amount of data that needs to be stored, the processing power required, and the necessary security measures. Organizations also need to consider factors such as energy efficiency, scalability, and redundancy to ensure that their data center can meet their needs in the long term.
Once the planning stage is complete, organizations can move on to the design and construction phase. This involves designing the layout of the data center, selecting the necessary hardware and software, and building the facility according to industry standards and best practices. It is important to ensure that the data center is built to withstand environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and power outages.
After the data center is up and running, organizations need to focus on the operational stage of lifecycle management. During this phase, IT professionals are responsible for monitoring and maintaining the data center to ensure that it is running efficiently and effectively. This includes performing regular maintenance tasks, monitoring performance metrics, and troubleshooting any issues that may arise. Organizations also need to implement security measures to protect their data from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
As technology evolves and data center requirements change, organizations may need to consider upgrading or expanding their data center infrastructure. This can involve adding new servers, storage devices, or networking equipment to meet the growing demands of the organization. It is important to carefully plan and execute these upgrades to minimize downtime and disruptions to business operations.
Finally, the last stage of data center lifecycle management is decommissioning. When a data center reaches the end of its useful life or when an organization decides to move to a new facility, the data center needs to be decommissioned properly. This involves safely removing and disposing of hardware, securely wiping data from storage devices, and ensuring that the facility is left in a safe and environmentally friendly condition.
In conclusion, data center lifecycle management is a complex and multi-faceted process that requires careful planning and execution at every stage. By following a comprehensive lifecycle management strategy, organizations can ensure that their data center infrastructure remains efficient, secure, and reliable throughout its lifespan. From planning and design to operation and decommissioning, each stage plays a crucial role in the overall success of a data center.