Data center storage has come a long way since the early days of computing. From bulky and slow tape drives to lightning-fast solid-state drives, the evolution of data center storage technology has been nothing short of remarkable.
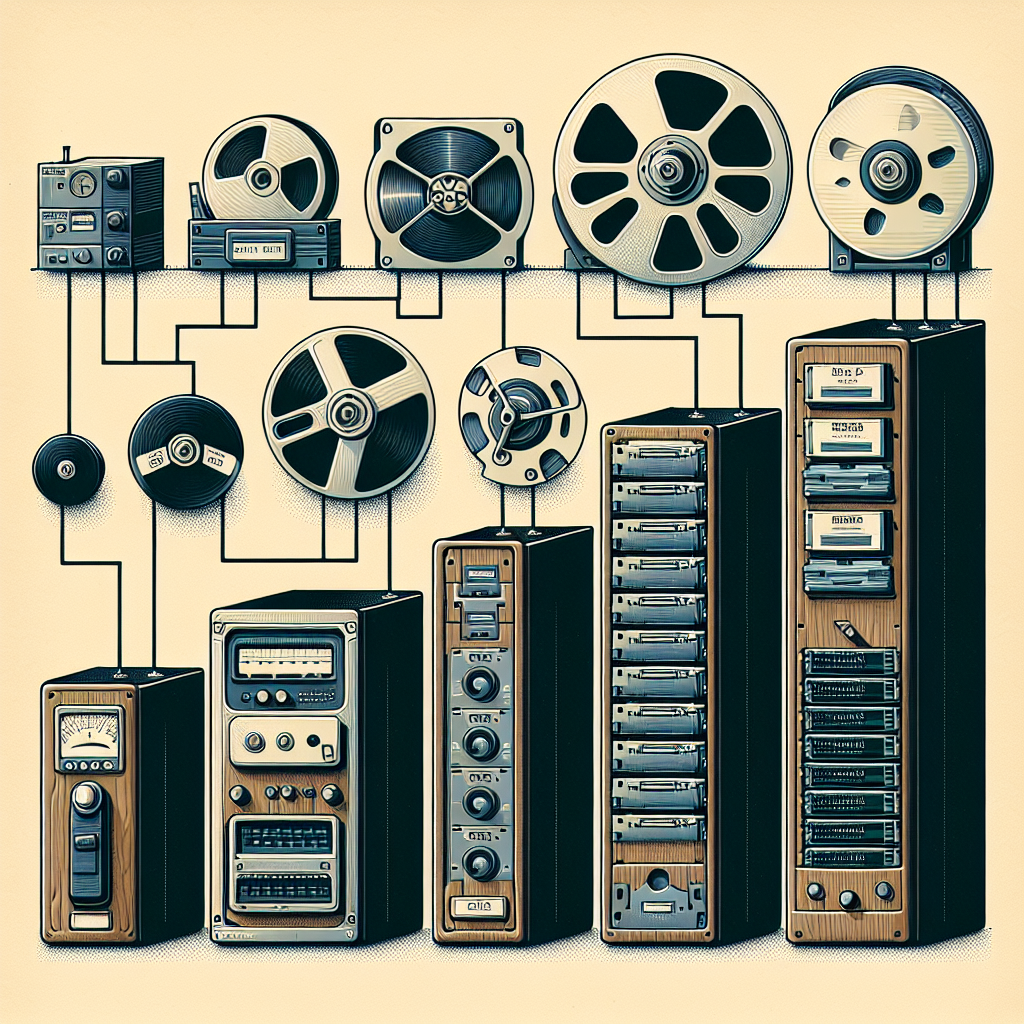
In the early days of computing, data was stored on magnetic tape drives. These drives were slow, unreliable, and had limited storage capacity. Data had to be physically rewound and fast-forwarded to access specific information, making data retrieval a time-consuming process. Despite their limitations, tape drives were the primary method of data storage for many years.
As technology advanced, the need for faster and more reliable storage solutions became apparent. This led to the development of hard disk drives (HDDs), which revolutionized data storage. HDDs use spinning disks to store data magnetically, allowing for faster access times and increased storage capacity. HDDs quickly became the standard storage solution for data centers and remain widely used today.
However, as data storage requirements continued to grow, the limitations of HDDs became more apparent. Solid-state drives (SSDs) emerged as a new and improved storage solution. SSDs use flash memory to store data, eliminating the need for spinning disks and significantly reducing access times. This results in faster read and write speeds, making SSDs ideal for high-performance applications.
SSDs also offer increased reliability and durability compared to HDDs, as they have no moving parts that can fail. This makes SSDs a popular choice for data centers where uptime and data integrity are critical.
The evolution of data center storage technology has also brought about advancements in storage architecture. Storage area networks (SANs) and network-attached storage (NAS) have become common solutions for managing and accessing large amounts of data in data centers. These technologies allow for centralized storage management and easier scalability, making it easier for organizations to store and access their data efficiently.
Looking ahead, the future of data center storage is likely to continue evolving. Emerging technologies such as non-volatile memory express (NVMe) and shingled magnetic recording (SMR) are poised to further improve storage performance and capacity. Additionally, the rise of cloud storage and software-defined storage solutions are changing the way data is stored and managed in data centers.
In conclusion, the evolution of data center storage from tape drives to solid-state drives has been a transformative journey. As technology continues to advance, data center storage solutions will only become faster, more reliable, and more efficient, enabling organizations to store and access their data more effectively than ever before.






You must be logged in to post a comment.