Price: $4,690.00
(as of Dec 03,2024 13:02:42 UTC – Details)

Fix today. Protect forever.
Secure your devices with the #1 malware removal and protection software
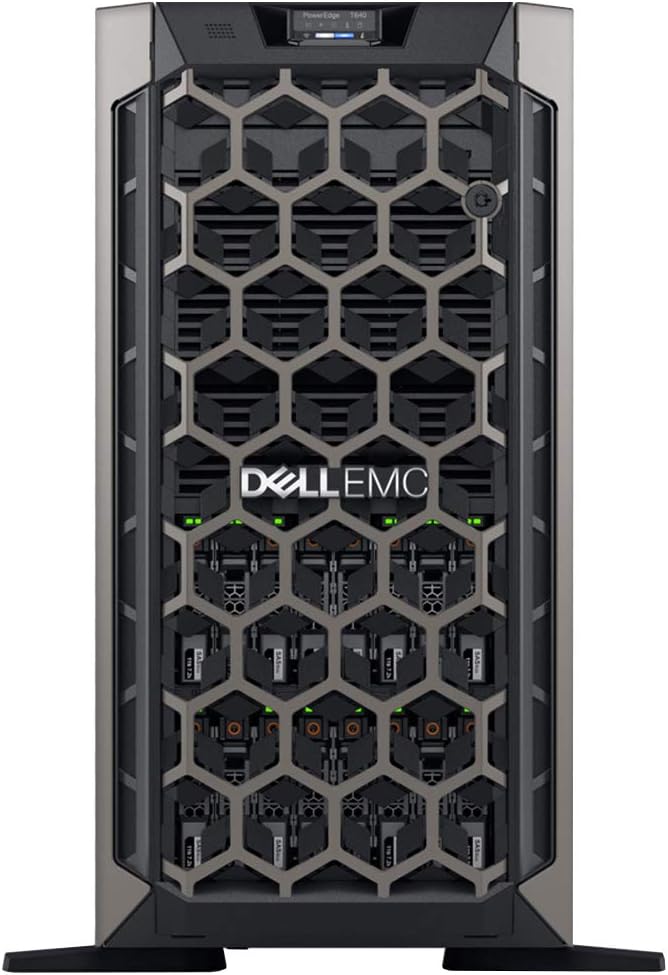
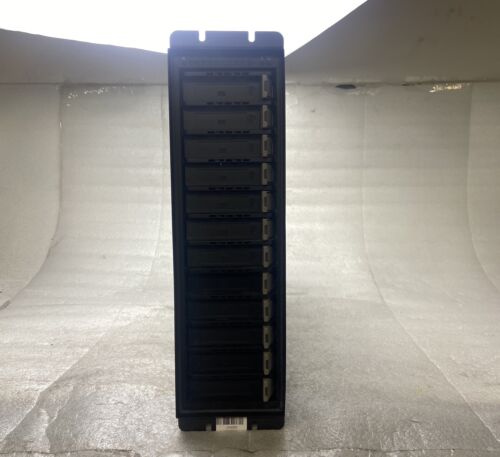
Dell PowerEdge T440 Tower Server for Small Businesses, Branch Locations, and Home Offices
Processors: Dual (2) Intel Silver 4110 8-Core 2.1GHz 11MB CPUs
Memory: 64GB DDR4 PC4-21300 2666MHz Registered Memory
Hard Drives: 8TB (4 x 2TB) 7.2K 12Gb/s SAS 3.5″ HDDs for High Capacity Storage
RAID: PERC H330 12Gb/s RAID Controller
Power: Redundant Power Supplies
Remote Access: iDRAC9 Express
Network Interface Card: On-Board Broadcom 5720 Dual Port 1Gb LOM
A Certified Refurbished product has been tested and certified to work and look like new, with minimal to no signs of wear, by a manufacturer or specialized third-party seller approved by Amazon. The product is backed by a minimum 90-day warranty, and may arrive in a generic brown or white box.
Dell PowerEdge T440 Tower Server for Small Businesses, Branch Locations, and Home Offices
Dual (2) Intel Silver 4110 8-Core 2.1GHz 11MB CPUs; 64GB DDR4 PC4-21300 2666MHz Registered Memory
8TB (4 x 2TB) 7.2K 12Gb/s SAS 3.5″ HDDs for High Capacity Storage; PERC H330 12Gb/s RAID Controller
iDRAC9 Express; On-Board Broadcom 5720 Dual Port 1Gb LOM
Fix today. Protect forever.
Secure your devices with the #1 malware removal and protection software
Looking for a powerful and reliable server for your business needs? Look no further than the Dell PowerEdge T440 Tower Server with 2 Intel Silver 4110 8-core CPUs. This renewed server comes with 64GB DDR4 RAM, 8TB 12Gb SAS HDDs, and RAID capabilities, making it perfect for handling demanding workloads and data storage requirements.
With dual Intel Silver 4110 CPUs, this server offers exceptional performance for multi-threaded applications and virtualization. The 64GB of DDR4 RAM ensures smooth and efficient operation, while the 8TB 12Gb SAS HDDs provide ample storage space for your data. The RAID functionality offers data protection and redundancy, ensuring your critical information is safe and secure.
Whether you need a server for running applications, hosting websites, or storing large amounts of data, the Dell PowerEdge T440 Tower Server is up to the task. Don’t miss out on this great deal on a high-quality, renewed server that will meet your business needs and exceed your expectations.
#Dell #PowerEdge #T440 #Tower #Server #Intel #Silver #8core #CPUs #64GB #DDR4 #8TB #12Gb #SAS #HDDs #RAID #Renewed