Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Heads
The Role of Read-Write Heads in Data Recovery and Backup Solutions
Data recovery and backup solutions are essential tools for protecting and preserving important information stored on electronic devices. One crucial component of these solutions is the read-write heads, which play a vital role in the process of retrieving and storing data.Read-write heads are tiny components located inside a hard drive or other storage device that are responsible for reading and writing data on the storage medium. When data is stored on a device, the read-write heads move back and forth across the surface of the storage medium, reading and writing data as needed. This process allows the device to access and store information quickly and efficiently.
In the event of data loss or corruption, read-write heads are instrumental in the data recovery process. When data is lost or becomes inaccessible, specialized software and hardware can be used to retrieve the information from the storage medium. The read-write heads play a crucial role in this process by physically accessing the storage medium and retrieving the lost data.
In addition to data recovery, read-write heads are also essential for creating backups of important information. By writing data to a storage medium, such as an external hard drive or cloud server, read-write heads ensure that important information is safely stored and can be easily accessed in the event of data loss.
Overall, read-write heads are essential components of data recovery and backup solutions. Without these tiny components, it would be nearly impossible to access and retrieve important information stored on electronic devices. By understanding the role of read-write heads in data recovery and backup solutions, individuals and businesses can better protect and preserve their valuable information.
The Importance of Proper Maintenance for Read-Write Heads in Storage Devices
Storage devices are an essential part of our daily lives, whether it’s our computers, smartphones, or external hard drives. These devices store our valuable data, from important documents and photos to music and videos. However, many of us may not realize the importance of proper maintenance for the read-write heads in these storage devices.The read-write heads are crucial components of storage devices, as they are responsible for reading and writing data on the magnetic disks inside the device. Without properly functioning read-write heads, the device may not be able to access or save data, leading to potential data loss.
Proper maintenance of read-write heads is essential to ensure the longevity and reliability of storage devices. Here are some reasons why it is important to maintain the read-write heads:
1. Preventing data loss: If the read-write heads become dirty or damaged, they may not be able to read or write data properly. This can result in data corruption or loss, which can be devastating, especially if the data is irreplaceable.
2. Improving performance: Clean and well-maintained read-write heads can help improve the performance of storage devices. By ensuring the read-write heads are in good condition, data transfer speeds can be optimized, allowing for faster access to files and applications.
3. Extending the lifespan of the device: Regular maintenance of read-write heads can help extend the lifespan of storage devices. By keeping the heads clean and free of debris, they are less likely to wear out quickly, prolonging the overall lifespan of the device.
4. Avoiding costly repairs: Neglecting maintenance of read-write heads can lead to more serious issues that may require costly repairs or even the replacement of the entire device. By taking proactive steps to maintain the heads, you can avoid these unnecessary expenses.
So, how can you properly maintain the read-write heads in your storage devices? Here are some tips:
– Keep the device clean: Dust and debris can accumulate on the read-write heads, affecting their performance. Regularly clean the device using a soft, dry cloth to remove any buildup.
– Avoid physical damage: Be careful when handling the storage device to avoid dropping or bumping it, which can damage the read-write heads.
– Use the device properly: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for using and storing the device to ensure the read-write heads are not subjected to unnecessary wear and tear.
In conclusion, proper maintenance of read-write heads in storage devices is crucial for ensuring data integrity, performance, and longevity. By following these tips and taking care of your storage devices, you can prevent data loss, improve performance, and extend the lifespan of your devices.

How Read-Write Heads Impact the Performance and Efficiency of Storage Devices
Read-write heads are a crucial component of storage devices such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). These small, electromechanical devices are responsible for reading and writing data on the storage media, allowing users to access and store information efficiently.The performance and efficiency of storage devices are greatly impacted by the quality and design of their read-write heads. The speed at which data can be read or written, as well as the overall reliability of the device, is directly influenced by the performance of these heads.
In HDDs, the read-write heads are mounted on an actuator arm that moves across the spinning disk platter to access different data tracks. The precision and speed of this movement, as well as the accuracy of the heads in reading and writing data, play a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the drive. High-quality read-write heads can improve data transfer speeds, reduce latency, and enhance the overall efficiency of the storage device.
In SSDs, the read-write heads are typically integrated into the controller chip, which manages the data storage and retrieval process. The efficiency of the read-write heads in SSDs is crucial for maximizing the performance of the drive, as they directly impact the speed at which data can be accessed and transferred.
Additionally, the design of the read-write heads can also affect the durability and longevity of storage devices. Poorly designed heads can cause data corruption, data loss, and premature drive failure. On the other hand, high-quality heads can improve the reliability and lifespan of the storage device, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring a longer operational lifespan.
Overall, the performance and efficiency of storage devices are heavily dependent on the quality and design of their read-write heads. Investing in high-quality, well-designed heads can greatly improve the speed, reliability, and longevity of storage devices, providing users with a more efficient and effective storage solution.
The Evolution of Read-Write Heads in Hard Drives and Solid State Drives
Over the past few decades, the evolution of read-write heads in hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) has played a crucial role in the advancement of data storage technology. From the early days of magnetic recording to the modern era of flash memory, engineers have continually improved the performance and reliability of read-write heads to keep up with the growing demand for faster and more efficient storage solutions.In the early days of hard drives, read-write heads were composed of a thin layer of magnetic material that could detect and write data to the spinning platters inside the drive. These heads were relatively large and bulky, limiting the amount of data that could be stored on a single drive. As technology advanced, engineers were able to shrink the size of these heads, allowing for higher data densities and increased storage capacities.
One of the key advancements in read-write head technology came with the introduction of thin-film heads in the 1980s. These heads were made from a thin layer of magnetic material deposited on a non-magnetic substrate, allowing for greater precision and improved performance. Thin-film heads also helped reduce the size of the heads, enabling even higher data densities and faster access times.
In the 1990s, the introduction of giant magnetoresistive (GMR) heads revolutionized read-write head technology. GMR heads were able to detect smaller magnetic fields than previous technologies, leading to higher data densities and improved data reliability. This breakthrough allowed for the development of smaller and more efficient hard drives that could store even more data in a smaller physical footprint.
With the rise of SSDs in recent years, the need for read-write heads has shifted to a different type of technology. Instead of using magnetic materials to read and write data, SSDs use flash memory chips to store information. This eliminates the need for moving parts, making SSDs faster, more reliable, and more energy-efficient than traditional hard drives.
Despite the differences in technology, the evolution of read-write heads in hard drives and SSDs has been driven by the same goal: to increase storage capacity, improve performance, and enhance data reliability. As data storage needs continue to grow, engineers will continue to push the boundaries of read-write head technology to meet the demands of an increasingly digital world.
Enhancing Data Storage Efficiency with Advanced Read-Write Heads
In today’s digital age, data storage is becoming increasingly important as the amount of data being generated and stored continues to grow exponentially. With the need for more efficient and reliable data storage solutions, advancements in read-write head technology are playing a crucial role in enhancing data storage efficiency.Read-write heads are the components of a hard drive that read and write data to the magnetic platters within the drive. These heads are constantly in motion, moving back and forth across the platters to access and store data. As data storage technologies continue to evolve, the development of advanced read-write heads has become essential to improve data storage performance.
One of the key advancements in read-write head technology is the use of smaller and more precise components. By reducing the size of the read-write heads, data can be stored more densely on the platters, increasing the overall storage capacity of the drive. This allows for more data to be stored in a smaller physical space, making data storage more efficient and cost-effective.
Another important advancement in read-write head technology is the development of multi-layer read-write heads. These heads are capable of reading and writing data across multiple layers of the magnetic platters simultaneously, increasing data access speeds and overall performance. This technology allows for faster data transfer rates, reducing latency and improving the overall efficiency of data storage systems.
Additionally, advancements in read-write head technology have also led to improvements in data reliability and durability. With more precise and efficient read-write heads, data can be stored and accessed more reliably, reducing the risk of data loss or corruption. This is especially important in critical data storage applications, such as enterprise servers and data centers, where data integrity is paramount.
Overall, the development of advanced read-write heads is crucial for enhancing data storage efficiency in today’s digital world. By increasing storage capacity, improving data access speeds, and enhancing data reliability, these advancements are helping to drive innovation in data storage technology. As the demand for larger and more efficient data storage solutions continues to grow, the role of advanced read-write heads will only become more important in meeting these needs.

How Read-Write Heads Impact Data Access Speeds
When it comes to data storage in hard drives, read-write heads play a crucial role in determining how quickly data can be accessed and written. These small components are responsible for reading data from and writing data to the spinning platters inside a hard drive. The speed at which the read-write heads can move and access data directly impacts the overall performance of the hard drive.The first way in which read-write heads impact data access speeds is through their positioning and movement. The heads need to be able to quickly move to the correct position on the spinning platter in order to read or write data. The faster the read-write heads can move, the quicker data can be accessed. This is why hard drives with higher RPM (revolutions per minute) tend to have faster data access speeds, as the spinning platters allow the heads to move more quickly.
Another factor that affects data access speeds is the precision of the read-write heads. The heads need to be able to accurately read and write data on the platters, which requires precise positioning and alignment. If the heads are not able to accurately access data, it can result in slower data transfer speeds and potential data loss.
Additionally, the technology used in the read-write heads can also impact data access speeds. Newer technologies, such as perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) and shingled magnetic recording (SMR), allow for higher data densities and faster data transfer speeds. These technologies enable the read-write heads to access more data in a shorter amount of time, resulting in improved performance.
Overall, the read-write heads in a hard drive play a critical role in determining how quickly data can be accessed and written. Factors such as positioning, movement, precision, and technology all contribute to the overall data access speeds of a hard drive. By understanding how read-write heads impact data access speeds, users can make informed decisions when selecting a hard drive for their storage needs.
How Read-Write Heads Work: A Closer Look at Data Retrieval
When you save a file on your computer or access information from a hard drive, you may not think about the intricate process that occurs behind the scenes to retrieve that data. One crucial component of this process is the read-write head, a small but essential part of the hard drive that plays a vital role in data retrieval.So, how do read-write heads work? Let’s take a closer look at this fascinating technology.
Read-write heads are tiny electromagnets located at the tip of the actuator arm inside a hard drive. These heads are responsible for reading and writing data to and from the magnetic platters that make up the hard drive. When you save a file, the data is converted into a series of magnetic impulses that are then written to the platters by the read-write heads. When you access that file later, the read-write heads read the magnetic impulses from the platters and convert them back into the original data.
The read-write heads work by using a process called magnetic recording. This process involves aligning the magnetic domains on the platters in a specific pattern to represent the data being stored. When writing data, the read-write heads generate a magnetic field that aligns the domains on the platters in the desired pattern. When reading data, the heads detect the magnetic fields on the platters and translate them into the original data.
To ensure accurate data retrieval, the read-write heads must be extremely precise in their movements. They must be able to move quickly and accurately across the surface of the platters to access the data stored on them. The actuator arm, which holds the read-write heads, is controlled by a mechanism that positions the heads over the correct location on the platters.
In addition to precision, read-write heads must also be able to operate in a highly controlled environment. Hard drives are sealed to prevent dust and other contaminants from entering and interfering with the heads’ movements. The heads themselves are also designed to be resistant to external magnetic fields that could disrupt their ability to read and write data.
Overall, read-write heads are a crucial component of the data retrieval process in a hard drive. Without these tiny electromagnets, we would not be able to store and access the vast amounts of data that we rely on in our daily lives. The next time you save a file or access information from your computer, take a moment to appreciate the intricate technology at work behind the scenes, making it all possible.

The Evolution of Read-Write Heads: From Floppy Disks to Solid State Drives
The Evolution of Read-Write Heads: From Floppy Disks to Solid State DrivesThe development of read-write heads has played a crucial role in the advancement of storage technology over the years. From the early days of floppy disks to the modern solid state drives, read-write heads have undergone significant evolution to meet the increasing demands for faster and more reliable data storage solutions.
In the early days of computing, floppy disks were the primary method of storing data. These magnetic storage devices used read-write heads to read and write data on the disk. The read-write heads would move across the disk’s surface, magnetizing and demagnetizing tiny regions to store data. However, floppy disks had limited storage capacity and were prone to data loss due to their fragile nature.
As technology advanced, hard disk drives (HDDs) emerged as a more reliable and higher-capacity storage solution. HDDs also used read-write heads to access and store data on spinning platters coated with a magnetic material. The read-write heads would float just above the spinning platters, reading and writing data as needed. This technology allowed for faster data access and greater storage capacity than floppy disks.
In recent years, solid state drives (SSDs) have become increasingly popular due to their faster read and write speeds, lower power consumption, and greater durability. SSDs do not have moving parts like HDDs, eliminating the need for read-write heads to physically move across spinning platters. Instead, SSDs use flash memory to store data, allowing for faster access times and improved reliability.
The evolution of read-write heads from floppy disks to solid state drives has been driven by the need for faster, more reliable, and higher-capacity storage solutions. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that read-write heads will continue to evolve to meet the growing demands for data storage in an increasingly digital world.
Overall, the evolution of read-write heads has played a crucial role in shaping the way we store and access data. From the humble beginnings of floppy disks to the cutting-edge technology of solid state drives, read-write heads have come a long way in meeting the ever-changing needs of data storage.

Maximizing the Lifespan of Read-Write Heads in Your Storage Devices
Storage devices are essential components of any computer system, allowing users to store and access their data efficiently. One crucial part of these devices is the read-write head, which is responsible for reading and writing data on the storage medium. Maximizing the lifespan of these read-write heads is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of your storage devices.Here are some tips to help you maximize the lifespan of read-write heads in your storage devices:
1. Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or mishandling your storage devices, as this can cause damage to the read-write heads. Always use caution when handling and transporting your devices to prevent any physical damage.
2. Keep Your Devices Clean: Dust and debris can accumulate on the read-write heads, affecting their performance and lifespan. Regularly clean your storage devices with a soft, lint-free cloth to remove any dirt and dust.
3. Avoid Overloading: Avoid overloading your storage devices with too much data, as this can put strain on the read-write heads and reduce their lifespan. Keep your devices well-organized and avoid storing unnecessary files to prolong the lifespan of the read-write heads.
4. Use Quality Storage Media: Using high-quality storage media can help prevent premature wear and tear on the read-write heads. Invest in reputable brands and avoid using cheap or low-quality storage media that can cause damage to the read-write heads.
5. Properly Eject Devices: Always properly eject your storage devices from your computer before removing them to prevent damage to the read-write heads. Improperly ejecting devices can cause the heads to crash into the storage medium, leading to damage and data loss.
6. Keep Your Devices Cool: Excessive heat can damage the read-write heads in your storage devices. Ensure that your devices are properly ventilated and keep them in a cool, dry environment to prevent overheating and prolong the lifespan of the read-write heads.
By following these tips, you can maximize the lifespan of the read-write heads in your storage devices and ensure optimal performance and longevity. Taking care of your storage devices will not only save you time and money in the long run but also protect your valuable data from loss or corruption.
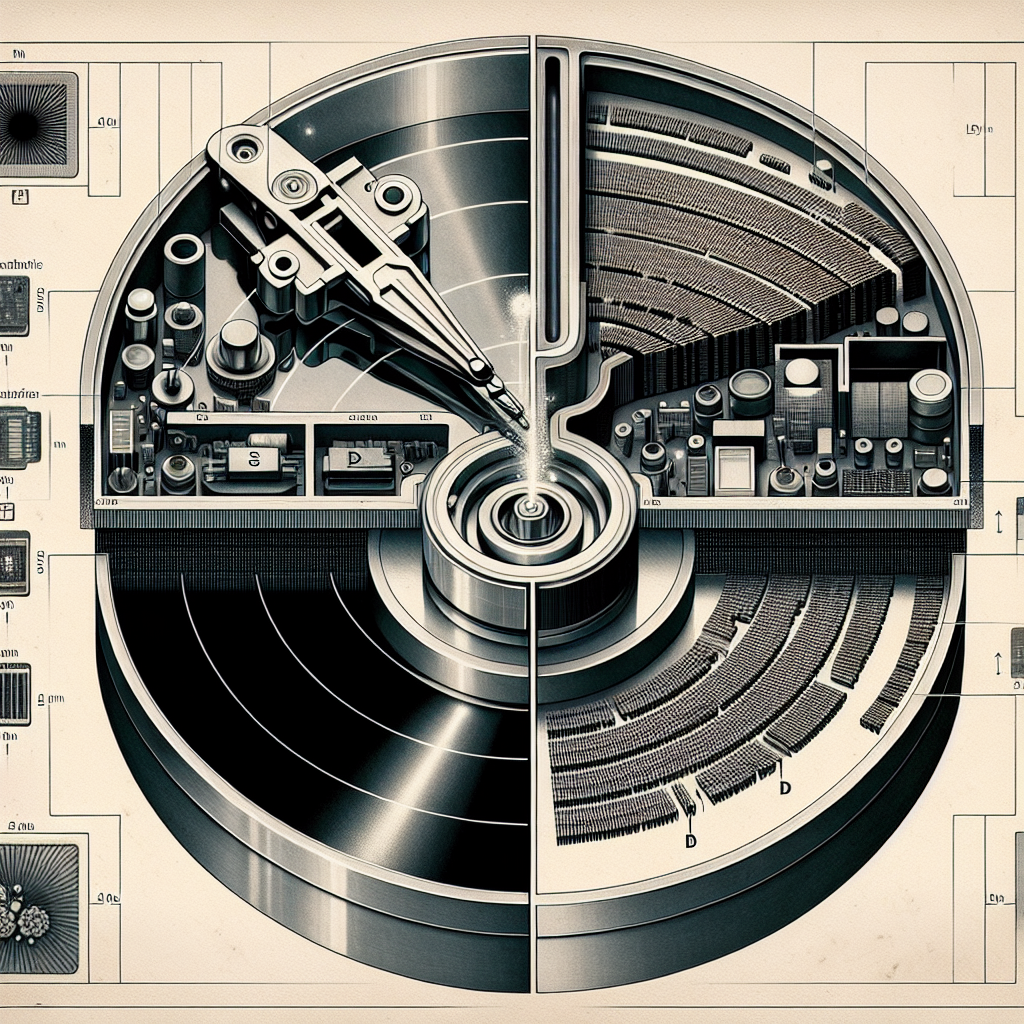
Exploring the Mechanics of Read-Write Heads in Magnetic and Solid State Storage
When it comes to storing data on a computer, there are two main types of storage devices: magnetic and solid-state drives. Both types of drives use read-write heads to access and store data, but the mechanics behind how these heads work differ significantly. In this article, we will explore the mechanics of read-write heads in both magnetic and solid-state storage devices.Magnetic storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs), have been around for decades and are still widely used today. These drives store data on spinning disks coated with a magnetic material. The read-write head in an HDD is a small electromagnetic device that moves back and forth across the surface of the disk to read and write data. When writing data, the read-write head generates a magnetic field that aligns the magnetic particles on the disk in a specific pattern. When reading data, the head detects the orientation of the magnetic particles and translates it into binary code.
The movement of the read-write head in an HDD is controlled by an actuator arm, which is connected to a motor. The arm moves the head to the correct position on the disk to access the data. The speed at which the head can move across the disk, known as the seek time, is a critical factor in the performance of an HDD. The faster the seek time, the quicker the drive can access and retrieve data.
In contrast, solid-state drives (SSDs) use flash memory to store data, eliminating the need for moving parts like the read-write head in an HDD. Instead, data is stored on interconnected memory chips that can be accessed simultaneously, allowing for faster read and write speeds. The absence of moving parts also makes SSDs more durable and less prone to mechanical failure.
In an SSD, the read-write process is controlled by a controller chip that manages data transfer between the memory chips and the computer’s processor. When writing data, the controller chip sends electrical signals to the memory cells to store the data in a specific location. When reading data, the controller retrieves the data from the memory cells and sends it to the processor. The lack of moving parts in an SSD results in faster access times and improved overall performance compared to HDDs.
In conclusion, the mechanics of read-write heads in magnetic and solid-state storage devices differ significantly. HDDs rely on a moving read-write head and spinning disks to access and store data, while SSDs use flash memory and a controller chip to achieve faster read and write speeds. Both types of drives have their advantages and disadvantages, but as technology continues to advance, SSDs are becoming increasingly popular due to their speed, reliability, and durability.
